- A dataset with test inputs and optionally expected outputs.
- A target function that defines what you’re evaluating. For example, this may be one LLM call that includes the new prompt you are testing, a part of your application or your end to end application.
- Evaluators that score your target function’s outputs.
This quickstart uses prebuilt LLM-as-judge evaluators from the open-source
openevals package. OpenEvals includes a set of commonly used evaluators and is a great starting point if you’re new to evaluations. If you want greater flexibility in how you evaluate your apps, you can also define completely custom evaluators using your own code.1. Install Dependencies
If you are using
yarn as your package manager, you will also need to manually install @langchain/core as a peer dependency of openevals. This is not required for LangSmith evals in general - you may define evaluators using arbitrary custom code.2. Create a LangSmith API key
To create an API key, head to the Settings page. Then click Create API Key.3. Set up your environment
Because this quickstart uses OpenAI models, you’ll need to set theOPENAI_API_KEY environment variable as well as the required LangSmith ones:4. Create a dataset
Next, define example input and reference output pairs that you’ll use to evaluate your app:5. Define what you’re evaluating
Now, define target function that contains what you’re evaluating. For example, this may be one LLM call that includes the new prompt you are testing, a part of your application or your end to end application.6. Define evaluator
Import a prebuilt prompt fromopenevals and create an evaluator. outputs are the result of your target function. reference_outputs / referenceOutputs are from the example pairs you defined in step 4 above.CORRECTNESS_PROMPT is just an f-string with variables for "inputs", "outputs", and "reference_outputs". See here for more information on customizing OpenEvals prompts.7. Run and view results
Finally, run the experiment!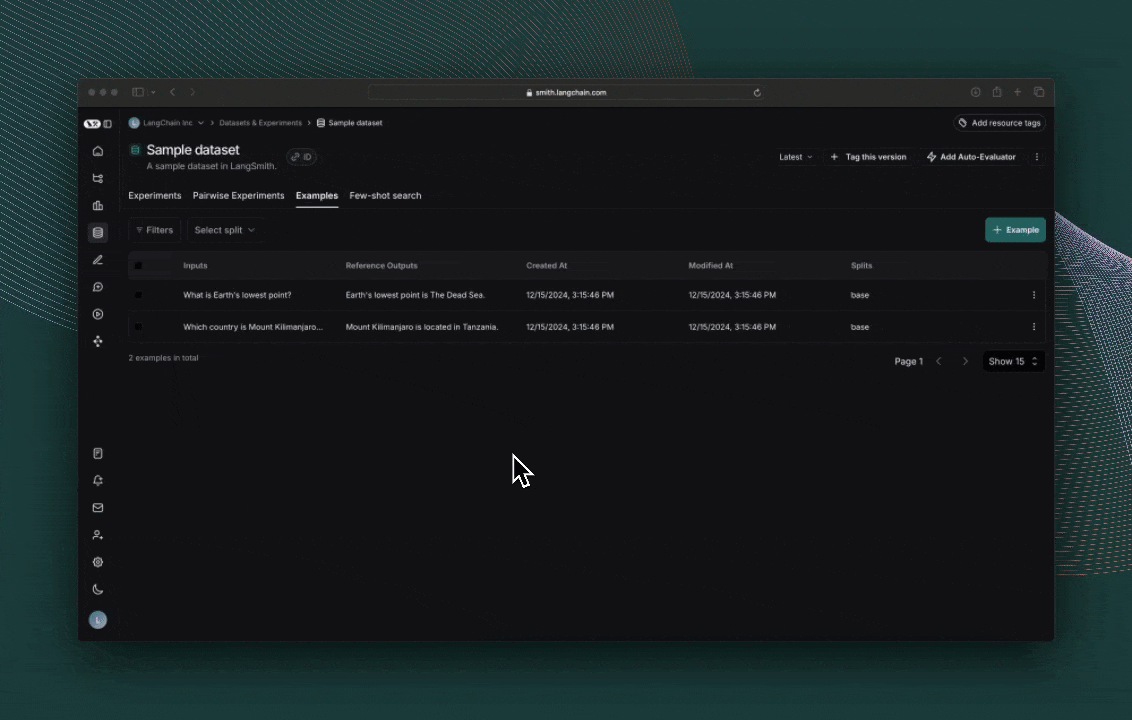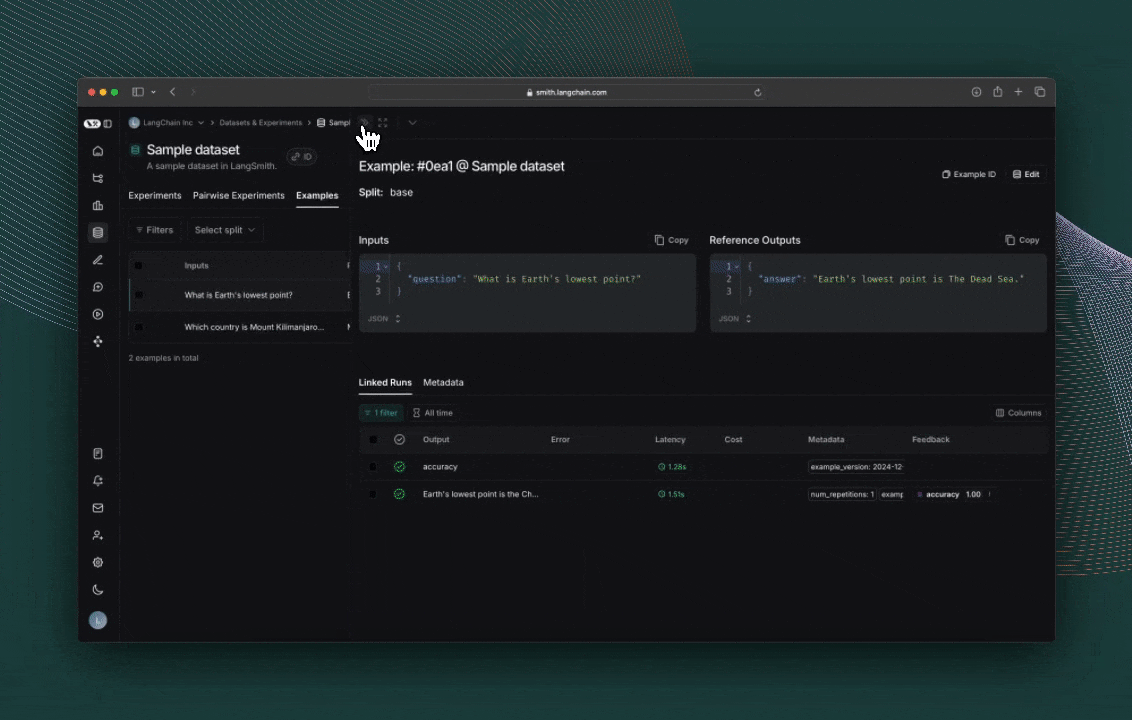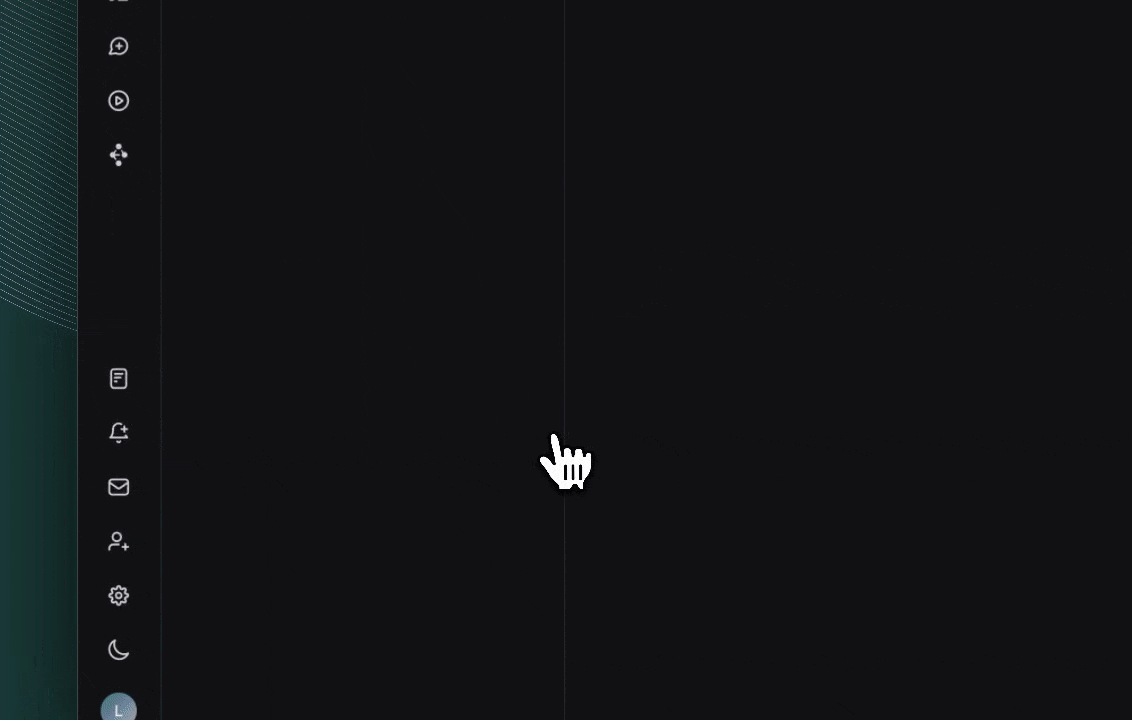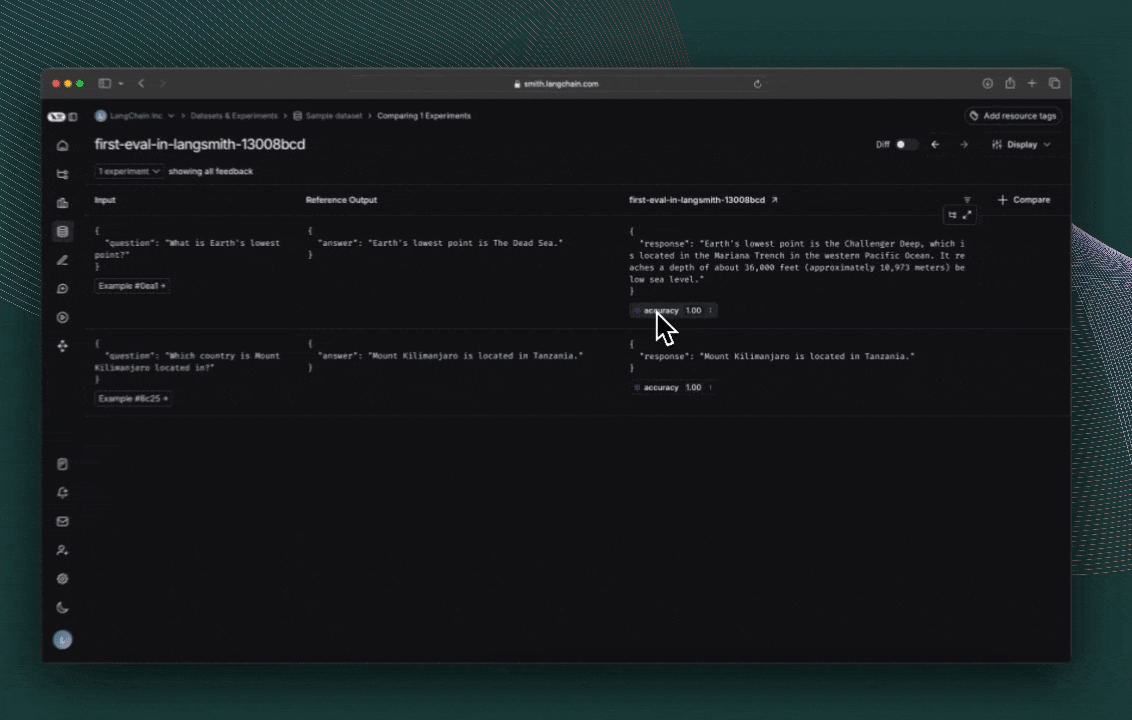
Next steps
To learn more about running experiments in LangSmith, read the evaluation conceptual guide.
- Check out the OpenEvals README to see all available prebuilt evaluators and how to customize them.
- Learn how to define custom evaluators that contain arbitrary code.
- For more details on evaluations, refer to the Evaluation documentation.
- For comprehensive descriptions of every class and function see the API reference.

