Installation
Install the core library and the OpenAI integration for Python and JS (we use the OpenAI integration for the code snippets below). For a full list of packages available, see the LangChain Python docs and LangChain JS docs.Quick start
1. Configure your environment
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=trueIf you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=falseSee this LangChain.js guide for more information.2. Log a trace
No extra code is needed to log a trace to LangSmith. Just run your LangChain code as you normally would.3. View your trace
By default, the trace will be logged to the project with the namedefault. An example of a trace logged using the above code is made public and can be viewed here.
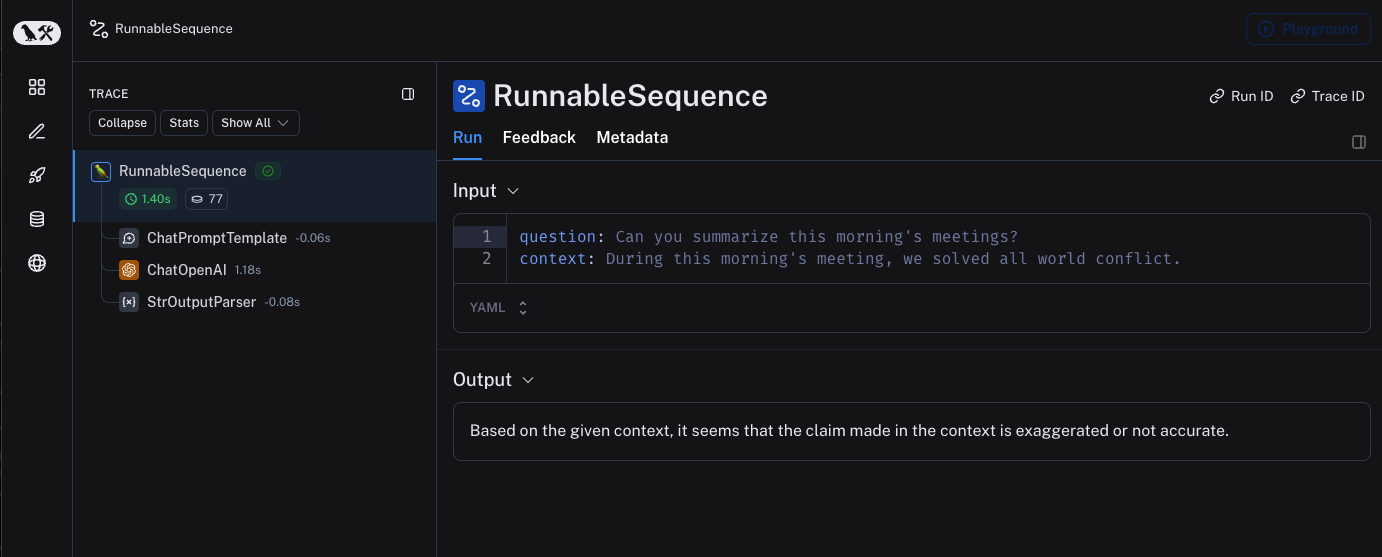
Trace selectively
The previous section showed how to trace all invocations of a LangChain runnables within your applications by setting a single environment variable. While this is a convenient way to get started, you may want to trace only specific invocations or parts of your application. There are two ways to do this in Python: by manually passing in aLangChainTracer (reference docs) instance as a callback, or by using the tracing_context context manager (reference docs).
In JS/TS, you can pass a LangChainTracer (reference docs) instance as a callback.
Log to a specific project
Statically
As mentioned in the tracing conceptual guide LangSmith uses the concept of a Project to group traces. If left unspecified, the tracer project is set to default. You can set theLANGSMITH_PROJECT environment variable to configure a custom project name for an entire application run. This should be done before executing your application.
The
LANGSMITH_PROJECT flag is only supported in JS SDK versions >= 0.2.16, use LANGCHAIN_PROJECT instead if you are using an older version.Dynamically
This largely builds off of the previous section and allows you to set the project name for a specificLangChainTracer instance or as parameters to the tracing_context context manager in Python.
Add metadata and tags to traces
You can send annotate your traces with arbitrary metadata and tags by providing them in the Config. This is useful for associating additional information with a trace, such as the environment in which it was executed, or the user who initiated it. For information on how to query traces and runs by metadata and tags, see this guideWhen you attach metadata or tags to a runnable (either through the RunnableConfig or at runtime with invocation params), they are inherited by all child runnables of that runnable.
Customize run name
You can customize the name of a given run when invoking or streaming your LangChain code by providing it in the Config. This name is used to identify the run in LangSmith and can be used to filter and group runs. The name is also used as the title of the run in the LangSmith UI. This can be done by setting arun_name in the RunnableConfig object at construction or by passing a run_name in the invocation parameters in JS/TS.
This feature is not currently supported directly for LLM objects.
Customize run ID
You can customize the ID of a given run when invoking or streaming your LangChain code by providing it in the Config. This ID is used to uniquely identify the run in LangSmith and can be used to query specific runs. The ID can be useful for linking runs across different systems or for implementing custom tracking logic. This can be done by setting arun_id in the RunnableConfig object at construction or by passing a run_id in the invocation parameters in JS/TS.
This feature is not currently supported directly for LLM objects.
trace_id).
Access run (span) ID for LangChain invocations
When you invoke a LangChain object, you can manually specify the run ID of the invocation. This run ID can be used to query the run in LangSmith. In JS/TS, you can use aRunCollectorCallbackHandler instance to access the run ID.
Ensure all traces are submitted before exiting
In LangChain Python, LangSmith’s tracing is done in a background thread to avoid obstructing your production application. This means that your process may end before all traces are successfully posted to LangSmith. This is especially prevalent in a serverless environment, where your VM may be terminated immediately once your chain or agent completes. You can make callbacks synchronous by setting theLANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND environment variable to "false".
For both languages, LangChain exposes methods to wait for traces to be submitted before exiting your application. Below is an example:
Trace without setting environment variables
As mentioned in other guides, the following environment variables allow you to configure tracing enabled, the api endpoint, the api key, and the tracing project:LANGSMITH_TRACINGLANGSMITH_API_KEYLANGSMITH_ENDPOINTLANGSMITH_PROJECT
Distributed tracing with LangChain (Python)
LangSmith supports distributed tracing with LangChain Python. This allows you to link runs (spans) across different services and applications. The principles are similar to the distributed tracing guide for the LangSmith SDK.Interoperability between LangChain (Python) and LangSmith SDK
If you are using LangChain for part of your application and the LangSmith SDK (see this guide) for other parts, you can still trace the entire application seamlessly. LangChain objects will be traced when invoked within atraceable function and be bound as a child run of the traceable function.
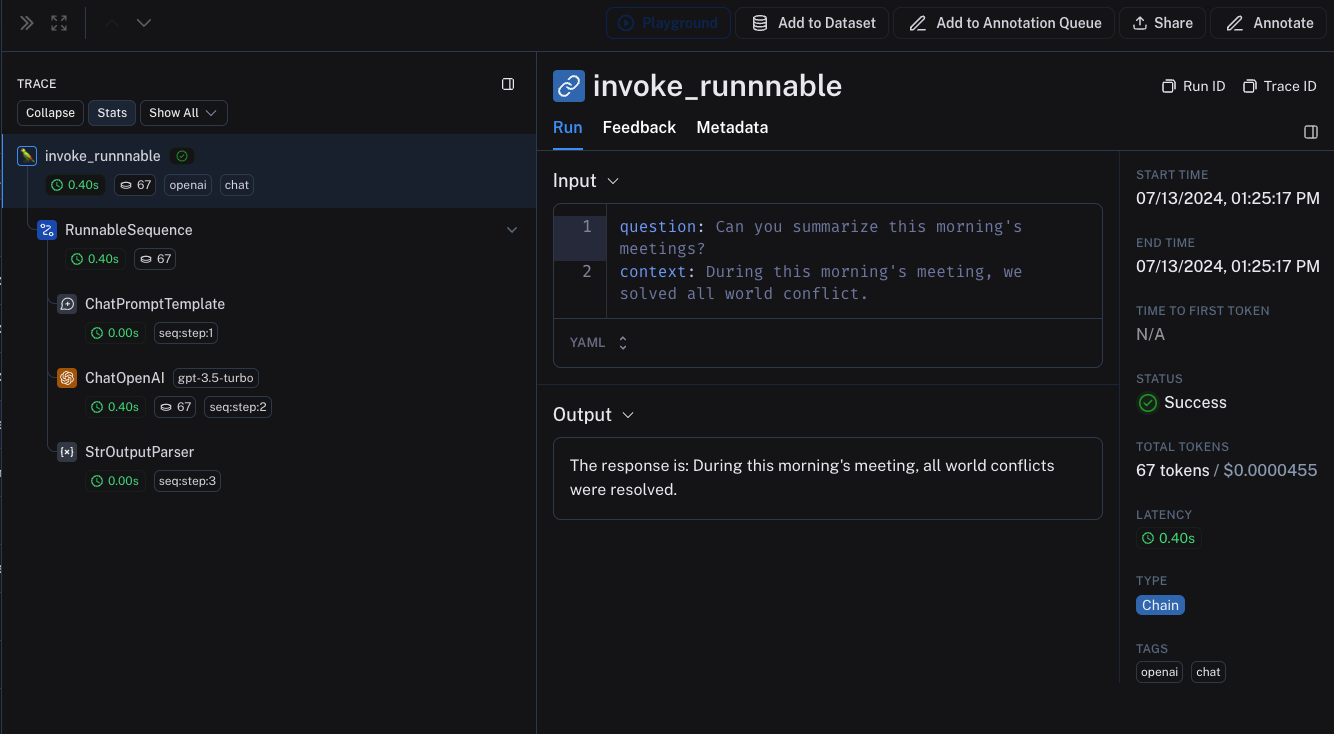
Interoperability between LangChain.JS and LangSmith SDK
Tracing LangChain objects inside traceable (JS only)
Starting with langchain@0.2.x, LangChain objects are traced automatically when used inside @traceable functions, inheriting the client, tags, metadata and project name of the traceable function.
For older versions of LangChain below 0.2.x, you will need to manually pass an instance LangChainTracer created from the tracing context found in @traceable.
Tracing LangChain child runs via traceable / RunTree API (JS only)
We’re working on improving the interoperability between
traceable and LangChain. The following limitations are present when using combining LangChain with traceable:- Mutating RunTree obtained from
getCurrentRunTree()of the RunnableLambda context will result in a no-op. - It’s discouraged to traverse the RunTree obtained from RunnableLambda via
getCurrentRunTree()as it may not contain all the RunTree nodes. - Different child runs may have the same
execution_orderandchild_execution_ordervalue. Thus in extreme circumstances, some runs may end up in a different order, depending on thestart_time.
traceable functions as part of the RunnableSequence or trace child runs of LangChain run imperatively via the RunTree API. Starting with LangSmith 0.1.39 and @langchain/core 0.2.18, you can directly invoke traceable-wrapped functions within RunnableLambda.
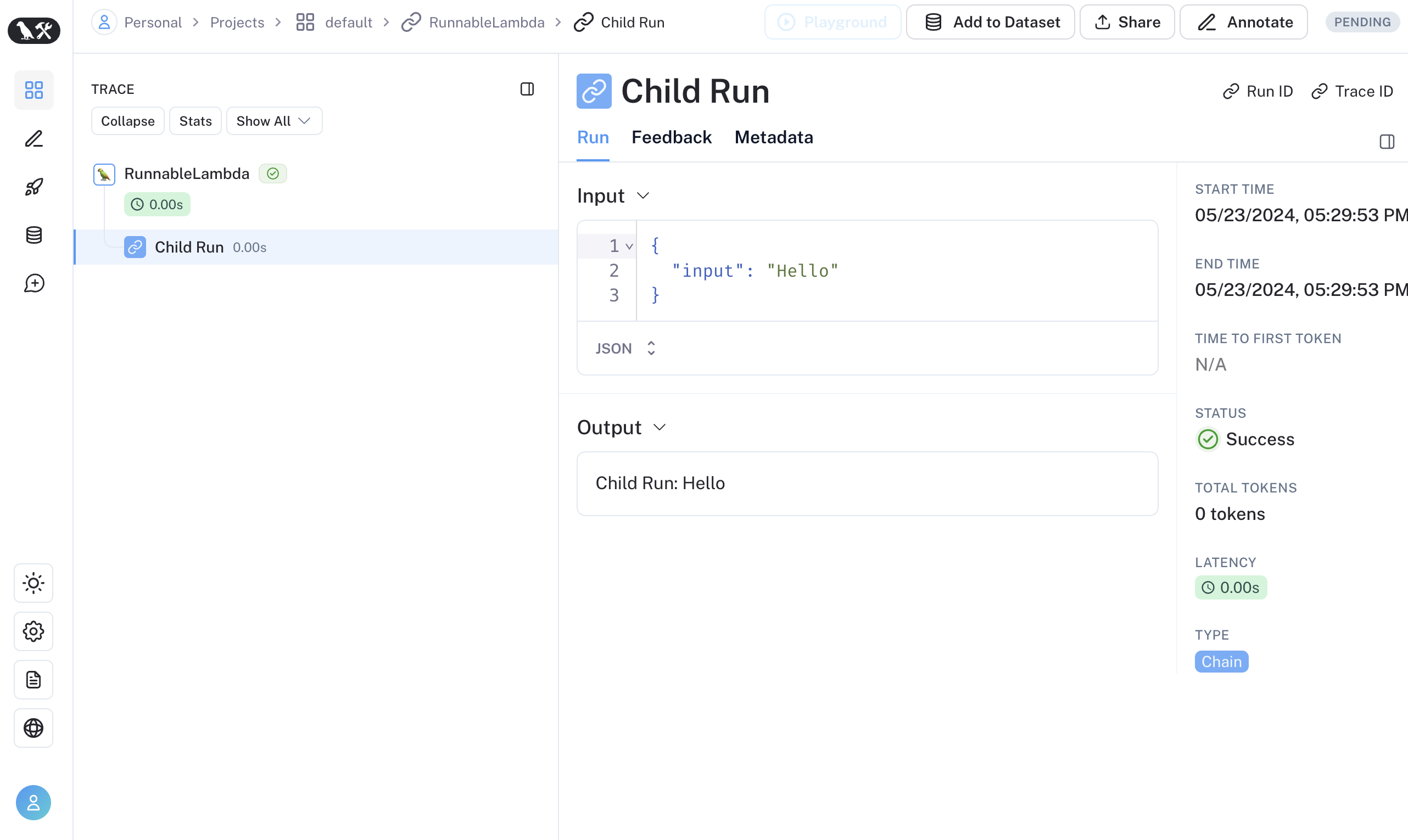 Alternatively, you can convert LangChain’s
Alternatively, you can convert LangChain’s RunnableConfig to a equivalent RunTree object by using RunTree.fromRunnableConfig or pass the RunnableConfig as the first argument of traceable-wrapped function.

