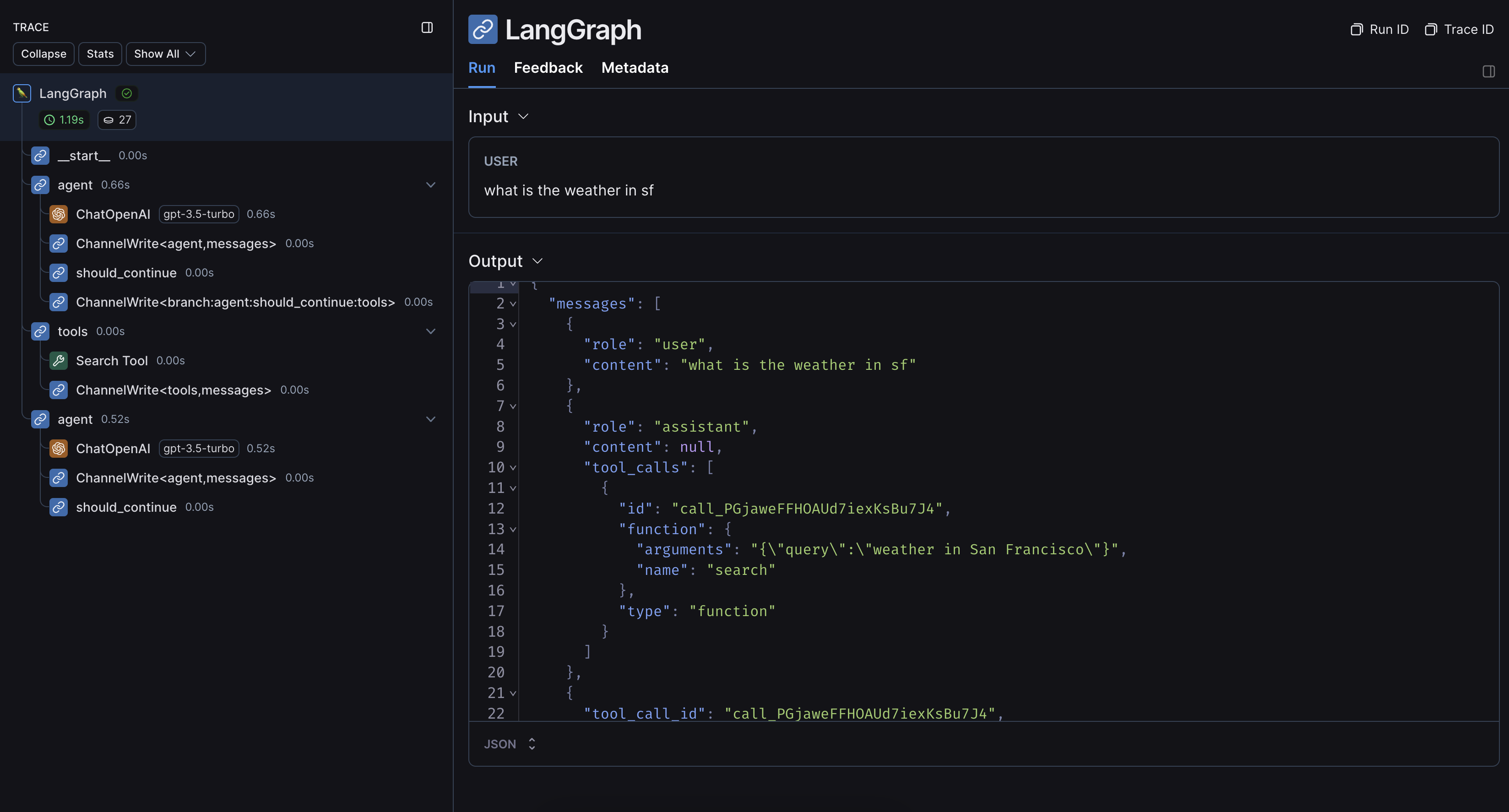
With LangChain
If you are using LangChain modules within LangGraph, you only need to set a few environment variables to enable tracing. This guide will walk through a basic example. For more detailed information on configuration, see the Trace With LangChain guide.1. Installation
Install the LangGraph library and the OpenAI integration for Python and JS (we use the OpenAI integration for the code snippets below). For a full list of packages available, see the LangChain Python docs and LangChain JS docs.- pip
- yarn
- npm
- pnpm
2. Configure your environment
- Python
- TypeScript
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=trueIf you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=falseSee this LangChain.js guide for more information.3. Log a trace
Once you’ve set up your environment, you can call LangChain runnables as normal. LangSmith will infer the proper tracing config:- Python
- TypeScript
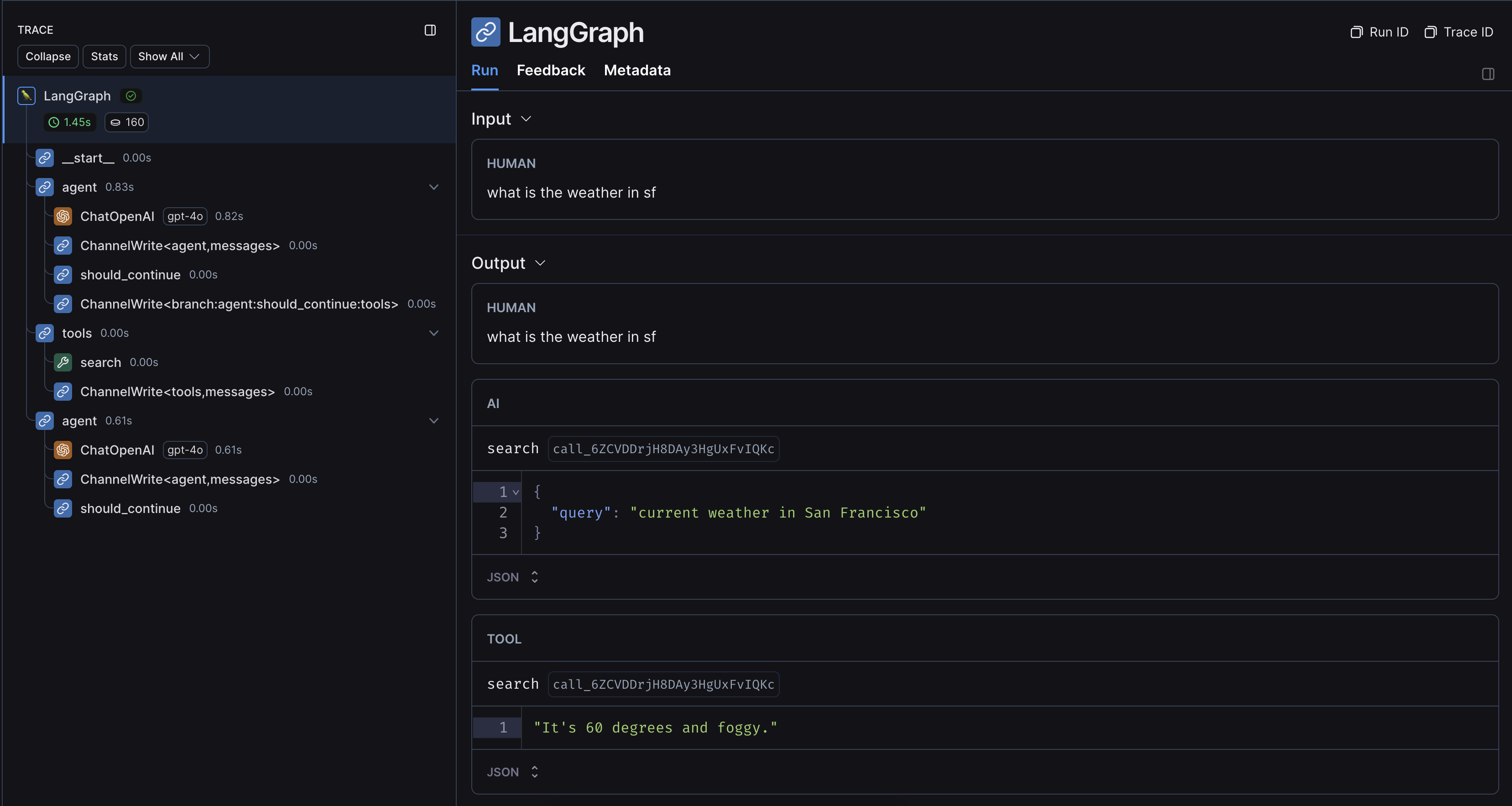
Without LangChain
If you are using other SDKs or custom functions within LangGraph, you will need to wrap or decorate them appropriately (with the@traceable decorator in Python or the traceable function in JS, or something like e.g. wrap_openai for SDKs). If you do so, LangSmith will automatically nest traces from those wrapped methods.
Here’s an example. You can also see this page for more information.
1. Installation
Install the LangGraph library and the OpenAI SDK for Python and JS (we use the OpenAI integration for the code snippets below).- pip
- yarn
- npm
- pnpm
2. Configure your environment
- Python
- TypeScript
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=trueIf you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=falseSee this LangChain.js guide for more information.3. Log a trace
Once you’ve set up your environment, wrap or decorate the custom functions/SDKs you want to trace. LangSmith will then infer the proper tracing config:- Python
- TypeScript